为什么要组件化
随着业务的发展,App中的页面,网络请求,通用弹层UI,通用TableCell数量就会剧增,需求的开发人员数量也会逐渐增多。
如果所有业务都在同一个App中,并且同时开发人数较少时,抛开代码健壮性不谈,实际的开发体验可能并没有那么糟糕,毕竟作为一个开发,什么地方用什么控件,就跟在HashMap中通过Key获取Value那么简单。
那么当业务成长到需要分化到多个App的时候,组件化的重要性开始体现了。
展示控件
@interface CESettingsCell : UITableViewCell
@property (strong, nonatomic) UILabel *titleLabel;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UILabel *tipsLabel;
@property (strong, nonatomic) UIImageView *arrowImgV;
@end
如代码所示这是一个很常见TableCell,其中有标题,小图标,右箭头。将这样的组件抽象成一个基类,后续再使用的时候,就可以直接继承改写,或者直接使用,能省去很多工作量。
随着页面的增加,这种结构会被大量的运用在其他列表之中。其实在第二相似需求出现的时候,就该考虑进行抽象的,可惜经常是忙于追赶业务,写着写着就给忘记了。
交互控件
@interface CEOptionPickerViewController : CEBaseViewController
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSArray<NSArray *> *pickerDataList;
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> *selectedIndexList;
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSString *tipsTitle;
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSDictionary *rowAttributes;
@property (copy, nonatomic) void(^didOptionSelectedBlock) (NSArray<NSNumber *> *selectedIndexList);
@end
这也是一个已经抽象好的控件,作用是显示一个内容为二维数组的选择器,可以用来选择省份-城市,或者年-月
这种类型的数据。
在组件中,这类一次编写,多场景使用组件是最容易抽象的,一般在第一次开发的时候就能想到组件化。需要注意的是,这样的组件尽量不要使用多层继承,如果有相同特性但是不同的实现,用Protocal将它们抽象出来。
牢记Copy-Paste是埋坑的开始(哈哈哈哈哈,你会忘记哪一份代码是最新的,血泪教训)。
基类与Category
基类并不鸡肋,合理使用,可以减少很多的重复代码,比如ViewController对StatusBar的控制,NavigationController对NavBar的控制。
这种全局都可能会用到的方法适合抽象到基类或Category中,避免重复代码。在抽象方法的时候一定要克制,确认影响范围足够广,实现方式比较普遍的实现才适合放入基类中,与业务相关的代码更需要酌情考虑。
比如一个定制化的返回键,在当前项目中属于通用方案,每个导航栏页面都用到了,但是如果新开了一个项目,是否是改个图片就继续用,还是连导航栏都可能自定义了呢。
这里举个例子,我们项目中用到了很多H5与Native的通信,于是就抽象了一个CEBaseWebViewController专门用来管理JS的注册与移除,以及基础Cookie设置。
网络数据层
我们现在采用的是MVVM模式,ViewModel的分层可以让ViewController中的数据交互都通过ViewModel来进行,ViewController与数据获取已经完全隔离。
另外我封装了一层网络层,用于对接服务端接口,进一步将ViewModel的网络依赖抽离出来。
// ViewController
@interface CEMyWalletViewController : CEBaseViewController
@property (strong, nonatomic) CEMyWalletViewModel *viewModel;
@end
// ViewModel
@interface CEMyWalletViewModel : NSObject
@property (assign, nonatomic) NSInteger currentPageIndex;
@property (assign, nonatomic) CEWalletBillFilterType filterType;
@property (strong, nonatomic) NSArray <CEWalletBillInfo *> *billList;
@property (strong, nonatomic) CEWallet *myWallet;
- (void)getMyWalletInfo:(BOOL)HUDVisible completion:(void(^)(BOOL success))completion;
- (void)getWalletShortBillInfoList:(void(^)(BOOL success))completion;
- (void)getWalletBillInfoList:(void(^)(BOOL success, BOOL hasMoreContent))completion;
@end
// Network
@interface CEWalletNetworking : NSObject
+ (void)getMyWalletDetail:(CENetworkingOption *)option completion:(CENetworkingCompletionBlock)completionBlock;
+ (void)getWalletShortBillList:(CENetworkingOption *)option completion:(CENetworkingCompletionBlock)completionBlock;
+ (void)getWalletBillListByPageNum:(NSInteger)pageNum billType:(CEWalletBillFilterType)billType option:(CENetworkingOption *)option completion:(CENetworkingCompletionBlock)completionBlock
@end
数据传输路径
Networking/Database -> ViewModel -> ViewController
用接口的形式将数据提供给ViewModel,ViewModel来维护ViewController的数据,ViewController只需要维护View的显示逻辑即可。
这样不论是服务端接口变更,还是业务逻辑变更,都不会影响到ViewController。
这里可以抽象的组件主要是在Networking和Database这一层,比如我在Networking对AFNetworking进行了二次封装,根据业务模块进行划分,方便业务使用。同样,Database我们用的是CoreData,也对其进行了二次封装。
ViewController的路由
方案选择
原先开发的时候,是为每一个页面都做了Category,作为路由逻辑的封装。缺点就是,比如像入口比较多的首页,就需要import多个Category。
学习了下网上流行的URLRouter,Protocol-Class和Target-Action方案,最后参考了Target-Action方案(传送门:CTMediator)的思路。
主要考虑到在后期会考虑升级成路由表,在Target-Action的调度者中加入Url方案也比较容易,参数解析已经完成,不需要重复修改。
实现方案
首先是将跳转逻辑统一管理起来,于是就又过了GHRouter。
GHRouter的主要作用是在运行时,请求页面的消息通过反射的形式传递到正确的RouteMap上,从而执行正确的跳转。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#define Router(targetClsName,selName,paramsDic) ([[GHRouter sharedInstance] performTargetClassName:(targetClsName) selectorName:(selName) params:(paramsDic)])
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface GHRouter : NSObject
/**
用于检测用于跳转的Url是否为特定Url,默认不检测
*/
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *openUrlScheme;
/**
targetClass 实例缓存
*/
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMapTable *targetCache;
/**
默认缓存30个target,超过阈值后,会随机移除一半。
*/
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger maxCacheTargetCount;
/**
默认检测targetClassName是否以“RouteMap”结尾,赋值为nil可以关闭检测。
*/
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *targetClassNameSuffix;
/**
默认检测selectorName是否以“routerTo”开头,赋值为nil可以关闭检测。
*/
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *selectorNamePrefix;
+ (instancetype)sharedInstance;
/**
通过URL跳转指定页面
例如:
MyProject://TargetClassName/SelectorName:?params1="phone"¶ms2="name"
或
MyProject://TargetClassName/SelectorName?params1="phone"¶ms2="name"
SelectorName后面可以不带冒号,会自动添加。
@param url 传入的URL
@param validate 自定义校验过程,传入nil,则表示不做自定义校验
@return 返回值
*/
- (id)performByUrl:(NSURL *)url validate:(BOOL(^)(NSURL *url))validate;
/**
例如:
在路由Class中创建以下方法,用于跳转。
为了规范用法,第一位参数必须传入NSDIctionary类型的对象。
- (UIViewController *)routerToViewController:(NSDictionary *)params;
- (void)routerToViewController:(NSDictionary *)params;
@param targetClassName 路由Class名称
@param selectorName 调用的路由方法
@param params 路由参数
@return 返回值
*/
- (id)performTargetClassName:(NSString *)targetClassName selectorName:(NSString *)selectorName params:( NSDictionary *__nullable)params;
- (void)removeTargetCacheByClassName:(NSString *)className;
- (void)cleanupTargetCache;
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import "GHRouter.h"
@implementation GHRouter
+ (instancetype)sharedInstance
{
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
static id sharedInstance = nil;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
sharedInstance = [[self alloc] init];
});
return sharedInstance;
}
- (instancetype)init
{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
[self setup];
}
return self;
}
- (void)dealloc
{
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] removeObserver:self];
}
- (void)setup
{
_targetCache = [NSMapTable strongToStrongObjectsMapTable];
_maxCacheTargetCount = 30;
_selectorNamePrefix = @"routeTo";
_targetClassNameSuffix = @"RouteMap";
_openUrlScheme = nil;
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(cleanupTargetCache) name:UIApplicationDidReceiveMemoryWarningNotification object:nil];
}
- (id)performByUrl:(NSURL *)url validate:(BOOL(^)(NSURL *url))validate
{
if (_openUrlScheme.length != 0) {
if (![url.scheme isEqualToString:_openUrlScheme]) {
return [NSNull null];
};
}
NSString *scheme = url.scheme;
if (scheme.length == 0) {
#ifdef DEBUG
NSLog(@"ERROR: %s url.scheme is nil",__FUNCTION__);
#endif
return [NSNull null];
}
NSString *targetClassName = url.host;
if (targetClassName.length == 0) {
#ifdef DEBUG
NSLog(@"ERROR: %s url.host is nil",__FUNCTION__);
#endif
return [NSNull null];
}
NSString *path = url.path;
if (path.length == 0) {
#ifdef DEBUG
NSLog(@"ERROR: %s url.path is nil",__FUNCTION__);
#endif
return [NSNull null];
}
if (validate) {
if (!validate(url)) {
return [NSNull null];
};
}
NSMutableString *selectorName = [NSMutableString stringWithString:path];
if ([selectorName hasPrefix:@"/"]) {
[selectorName deleteCharactersInRange:NSMakeRange(0, 1)];
}
if (![selectorName hasSuffix:@":"]) {
[selectorName stringByAppendingString:@":"];
}
NSDictionary *params = [self queryDictionary:url];
return [self performTargetClassName:targetClassName selectorName:selectorName params:params];
}
- (id)performTargetClassName:(NSString *)targetClassName selectorName:(NSString *)selectorName params:(NSDictionary *)params
{
NSAssert(targetClassName.length != 0, @"ERROR: %s \n targetClassName is nil",__FUNCTION__);
NSAssert(selectorName.length != 0, @"ERROR: %s \n selectorName is nil",__FUNCTION__);
NSAssert([selectorName hasSuffix:@":"], @"ERROR: %s \n selectorName (%@) must have params, such as \"routeToA:\"", __FUNCTION__, selectorName);
if (_targetClassNameSuffix.length != 0) {
NSAssert([targetClassName hasSuffix:_targetClassNameSuffix], @"ERROR: %s targetClassName must has suffix by \"%@\"",__FUNCTION__,_targetClassNameSuffix);
}
if (_selectorNamePrefix.length != 0) {
NSAssert([selectorName hasPrefix:_selectorNamePrefix], @"ERROR: %s selectorName must has Prefix by \"%@\"",__FUNCTION__,_selectorNamePrefix);
}
Class targetClass = NSClassFromString(targetClassName);
if (!targetClass) {
#ifdef DEBUG
NSLog(@"ERROR: %s targetClass can't found by targetClassName:\"%@\"",__FUNCTION__, targetClassName);
#endif
return [NSNull null];
}
id target = [_targetCache objectForKey:targetClassName];
if (!target) {
target = [[targetClass alloc] init];
}
SEL selector = NSSelectorFromString(selectorName);
if (![target respondsToSelector:selector]) {
#ifdef DEBUG
NSLog(@"ERROR:%s targetClassName:\"%@\" can't found selectorName:\"%@\"", __FUNCTION__, targetClassName, selectorName);
#endif
return [NSNull null];
}
#pragma clang diagnostic push
#pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Warc-performSelector-leaks"
return [self performTarget:target selector:selector params:params];
#pragma clang diagnostic pop
}
#pragma mark- Private Method
- (id)performTarget:(id)target selector:(SEL)selector params:(NSDictionary *)params
{
NSMethodSignature *method = [target methodSignatureForSelector:selector];
if (!method) {
return nil;
}
const char *returnType = [method methodReturnType];
//返回值如果非对象类型,会报EXC_BAD_ACCESS
if (strcmp(returnType, @encode(BOOL)) == 0) {
NSInvocation *invocation = [self invocationByMethod:method target:target selector:selector params:params];
[invocation invoke];
BOOL *result = malloc(method.methodReturnLength);
[invocation getReturnValue:result];
NSNumber *returnObj = @(*result);
free(result);
return returnObj;
} else if (strcmp(returnType, @encode(void)) == 0) {
NSInvocation *invocation = [self invocationByMethod:method target:target selector:selector params:params];
[invocation invoke];
return [NSNull null];
} else if (strcmp(returnType, @encode(unsigned int)) == 0
|| strcmp(returnType, @encode(NSUInteger)) == 0) {
NSInvocation *invocation = [self invocationByMethod:method target:target selector:selector params:params];
[invocation invoke];
NSUInteger *result = malloc(method.methodReturnLength);
[invocation getReturnValue:result];
NSNumber *returnObj = @(*result);
free(result);
return returnObj;
} else if (strcmp(returnType, @encode(double)) == 0
|| strcmp(returnType, @encode(float)) == 0
|| strcmp(returnType, @encode(CGFloat)) == 0) {
NSInvocation *invocation = [self invocationByMethod:method target:target selector:selector params:params];
[invocation invoke];
CGFloat *result = malloc(method.methodReturnLength);
[invocation getReturnValue:result];
NSNumber *returnObj = @(*result);
free(result);
return returnObj;
} else if (strcmp(returnType, @encode(int)) == 0
|| strcmp(returnType, @encode(NSInteger)) == 0) {
NSInvocation *invocation = [self invocationByMethod:method target:target selector:selector params:params];
[invocation invoke];
NSInteger *result = malloc(method.methodReturnLength);
[invocation getReturnValue:result];
NSNumber *returnObj = @(*result);
free(result);
return returnObj;
}
#pragma clang diagnostic push
#pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Warc-performSelector-leaks"
return [target performSelector:selector withObject:params];
#pragma clang diagnostic pop
}
- (NSInvocation *)invocationByMethod:(NSMethodSignature *)method target:(id)target selector:(SEL)selector params:(NSDictionary *)params
{
NSInvocation *invocation = [NSInvocation invocationWithMethodSignature:method];
[invocation setTarget:target];
[invocation setSelector:selector];
if (method.numberOfArguments > 2 && params) {
[invocation setArgument:¶ms atIndex:2];
}
return invocation;
}
#pragma mark Cache
- (void)addTargetToCache:(id)target targetClassName:(NSString *)targetClassName
{
// 当缓存数量达到上限的时候,会随机删除一半的缓存
if (_targetCache.count > _maxCacheTargetCount) {
while (_targetCache.count > _maxCacheTargetCount/2) {
[_targetCache removeObjectForKey:_targetCache.keyEnumerator.nextObject];
}
}
[_targetCache setObject:target forKey:targetClassName];
}
- (void)removeTargetCacheByClassName:(NSString *)className
{
[_targetCache removeObjectForKey:className];
}
- (void)cleanupTargetCache
{
[_targetCache removeAllObjects];
}
#pragma mark- Private Method
- (NSDictionary *)queryDictionary:(NSURL *)url
{
NSMutableDictionary *params = [[NSMutableDictionary alloc] init];
NSString *urlString = [url query];
for (NSString *param in [urlString componentsSeparatedByString:@"&"]) {
NSArray *elts = [param componentsSeparatedByString:@"="];
if ([elts count] < 2) {
continue;
}
[params setObject:[elts lastObject] forKey:[elts firstObject]];
}
return params;
}
@end
总结下Router通信流程
本地组件通信
Router收到请求,通过TargetClassName与SelectorName来寻找对应的Class与Selector,期间会校验TargetClassName是否以“RouteMap”结尾,SelectorName是否以“routeTo”,以规范和区分路由类。selector可以被响应后,会创建对应Class的对象(不用静态方法是因为静态方法在类加载的时候就会被初始化到内存中,而成员方法在实例初始化时才会被加载到内存中,使用静态方法会影响到启动速度),并加入缓存,通过methodSignatureForSelector获取对应的NSMethodSignature- 构建
NSInvocation并加入Params。 - 触发
NSInvocation,并获取返回值。对返回值进行判断,非对象类型的返回值包装成NSNumber,无返回值类型返回nil,以防止在获取返回值时出现Crash,或者类型出错。 - 当缓存的
Target达到阈值时,会被释放掉一半的缓存,当收到内存警告时,会释放掉所有的缓存。
远程通信
Router收到Url,先校验Scheme,再从Url中解析出TargetClassName、SelectorName和Params。- 进行自定义验证。
- 进入本地组件通信流程。
这里举个例子:比如有一个EditCompanyInfoViewController,首先要为EditInfoRouteMap,用于解析跳转参数。这里要注意的是,由于参数是包装在Dictionary中的,所以在route方法上请加上参数注释,方便后期维护。
// .h
@interface CEEditInfoRouteMap : NSObject
/**
跳转公司信息编辑页面
@param params @{@"completion":void (^completion)(BOOL success, UIViewController *vc)}
*/
- (void)routeToEditCompanyInfo:(NSDictionary *)params;
@end
// .m
#import "CEEditInfoRouteMap.h"
#import "CEEditCompanyInfoViewController.h"
@implementation CEEditInfoRouteMap
- (void)routeToEditCompanyInfo:(NSDictionary *)params
{
void (^completion)(BOOL success, UIViewController *vc) = params[@"completion"];
CEEditCompanyInfoViewController *vc = [[CEEditCompanyInfoViewController alloc] init];
[vc.viewModel getCompanyInfo:^(BOOL success) {
completion(success,vc);
}];
}
@end
再者为CERouter创建一个Category,用于管理路由构造。
// .h
#import "GHRouter.h"
@interface GHRouter (EditInfo)
- (void)routeToEditCompanyInfo:(void(^)(BOOL success, UIViewController *vc))completion;
@end
// .m
#import "GHRouter+EditInfo.h"
@implementation GHRouter (EditInfo)
- (void)routeToEditCompanyInfo:(void(^)(BOOL success, UIViewController *vc))completion
{
Router(@"CEEditInfoRouteMap", @"routeToEditCompanyInfo:", @{@"completion":completion});
}
@end
最终调用
#import "GHRouter+EditInfo.h"
- (void)editCompanyInfo
{
[[GHRouter sharedInstance] routeToEditCompanyInfo:^(BOOL success, UIViewController * _Nonnull vc) {
[self.navigationController pushViewController:vc animated:YES];
}];
}
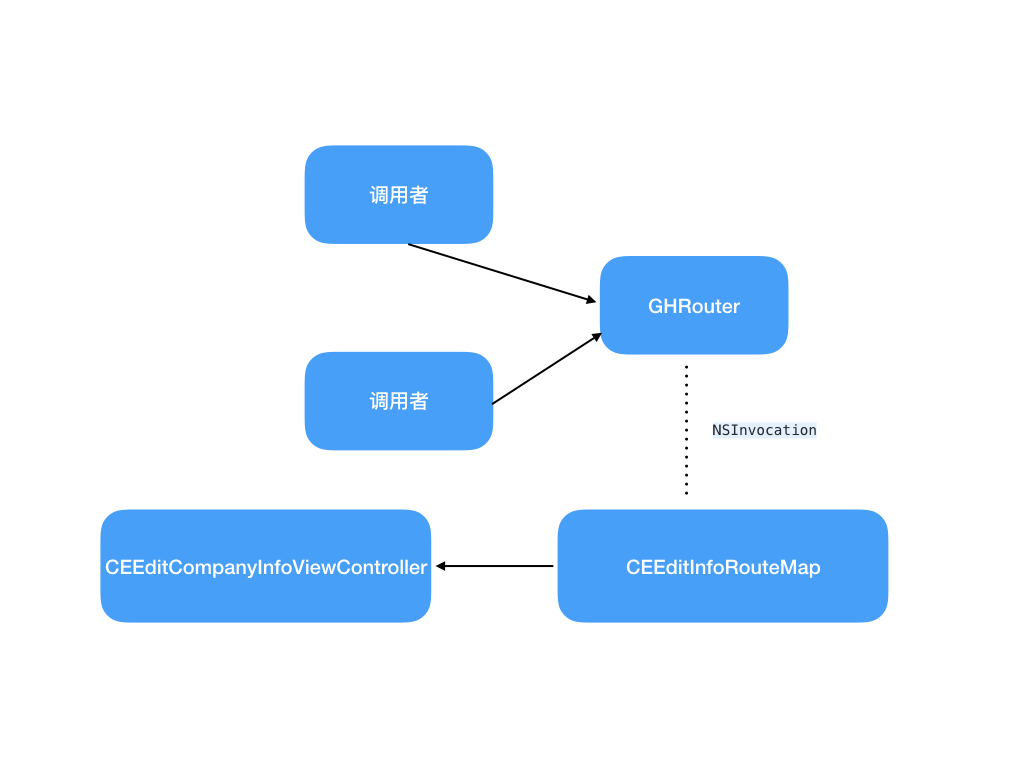
到这一步调用者依赖Router,Router通过NSInvocation与CEEditInfoRouteMap通信,CEEditInfoRouteMap依赖CEEditCompanyInfoViewController。
Router成为了单独的组件,没有依赖。
